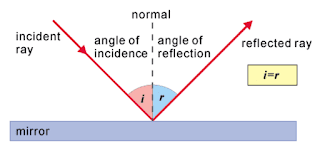
Reflection of light - When a ray of light strikes a polished surface, it bounces back in a particular direction. This is known as reflection of light. Laws of Reflection - The laws of reflection can be summarized as : 1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lies in the same plane. 2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Refraction of light - When a ray of light passes from one medium (say air) to another medium (say glass) of different optical density, it deviates from its original path. This is called refraction. Laws of Refraction - 1. The incident ray and the refracted ray are on the opposite sides of the normal at the point of incidence and all three lie in the same plane. 2. The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the Sine of angle of refraction is constant. This is known as snell's law. Sine ang...